File Descriptor
From COMP15212 Wiki
| On path: Filing | 1: Filing System • 2: File Systems • 3: Files • 4: File Attributes • 5: File Types • 6: File Permissions • 7: File Access • 9: Filing System Implementation • 10: I-nodes • 11: Links • 12: File Descriptor |
|---|
| Depends on | File Access • Filing System Implementation |
|---|
The descriptor will be created when a file is opened and is associated with a particular file within a particular process. It is used for immediate file access. It will hold information such as:
- the access permissions.
- e.g. whether you can currently read or write; different from the file access rights.
- the current position (index) in the file.
- the error status.
- control flags.
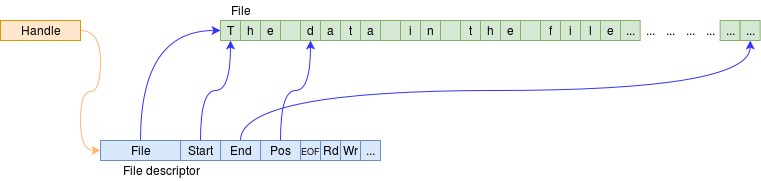
The details are deliberately kept opaque – loosely the equivalent of having private variables. A sketch (not 100% guaranteed!) is shown below. Do not try and memorise (or even understand!) all the details here – mostly marvel at the complexity!
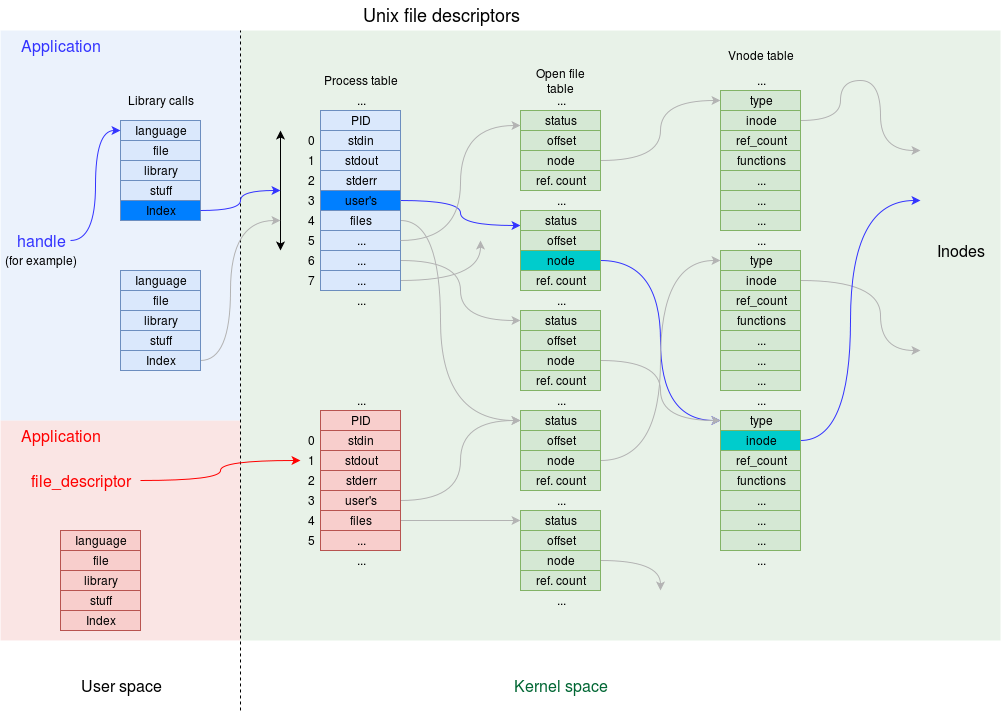
A couple of points:
- Unix maintains a simple table of files for each process.
- One file may be opened several times, simultaneously; each ‘opening’ has its own descriptor.
- Opened files can be shared: several processes can read the same file at the same time, for example.
- Eventually there is a pointer to the appropriate i-node.
File Descriptor vs. File Attributes
Like the file attributes, a file descriptor holds some metadata about a file. However these are not the same thing.
- The file attributes are ‘permanent’, in that they exist with the file; the file descriptor only exists whilst the file is in use.
- There is exactly one set of file attributes per file; there can be several file descriptors for the same file if it has been opened multiple times concurrently. Each descriptor will have (for example) its own file position.
| Also refer to: | Operating System Concepts, 10th Edition: Chapter 14.2.2, pages 568 |
|---|
Articles on Filing System
"Everything is a File" • FAT • File Access • File Attributes • File Descriptor • File Locking • File Permissions • File Systems • File Types • Files • Filing System • Filing System Implementation • Fragmentation • I-nodes • Journalling File System • Links • Network File System (NFS) • Resources