Arrays
From COMP15212 Wiki
| On path: Pointers | 1: Memory • 2: Arrays • 3: Pointers • 4: Pointer Exercise • 5: Structures • 6: Dynamic Memory Allocation • 7: Malloc Exercise • 8: Structs Exercise |
|---|
| Depends on | Memory |
|---|
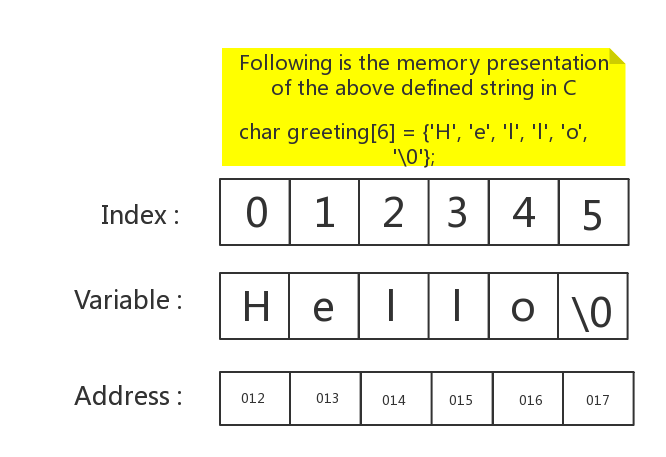
In C an array can be declared with int myArray[10];.
This creates an array of 10 integers, located at address myArray.
Normal array access is achieved thus:
myArray[0] = 5; // the first array element becomes 5
number = myArray[3]; // number becomes the fourth array element value
In C, arrays are just pointers to the first array element, myArray is just a ‘pointer to an integer’. See Pointer Arithmetic.
*(myArray) == myArray[0];
*(myArray + 3) == myArray[3];
An alias can use the array address too:
int *p_arr; // Create a pointer-to-int
p_arr = arr; // A copy of the array address
p_arr = &(arr[3]); // Point at a specific array element
Articles on Concepts
About this resource • Application Binary Interface (ABI) • Arrays • Atomicity • Boot • Cache • Cacheability • Caching • Concepts • Containers • Context • Context Switching • Deadlock • Direct Memory Access (DMA) • Environment Variables • Exceptions • File Attributes • Fragmentation • Hypervisor • Interrupts • Operation Ordering • PATH • Pointers • Process Scheduling • Processes • Processor Privilege • Queues • Real Time • Reentrancy • Relocatable Code • Spooling and Buffering • Synchronisation • Thrashing • Threads • Virtual Memory • VirtualisationArticles on Memory
About this resource • Arrays • Cache • Caching • Direct Memory Access (DMA) • Dirty Bit • Dynamic Memory Allocation • Memory • Memory Barrier • Memory Fault • Memory Leak • Memory Management • Memory Management Unit (MMU) • Memory Mapped Files • Memory Mapping • Memory Mapping Example • Memory Mapping Extra • Memory Pages • Memory Protection • Memory Segmentation • Memory Sizes • Monitoring page behaviour • Page Eviction • Paging • Paging States • Pointer Arithmetic • Pointers • Relocatable Code • Resources • Shared Memory • Structures • Translation Look-aside Buffer (TLB) • Virtual Memory • Write BufferArticles on User
"Everything is a File" • Application Binary Interface (ABI) • Arrays • Boot • Buffer Overflow • Containers • Daemons • Disk Partition • Dynamic Memory Allocation • Emulator traps • Environment Variables • Errors • Exceptions • File Attributes • File Locking • File Permissions • Introduction to Operating Systems • Journalling File System • Links • Locks • Man(ual pages in Unix) • Memory Mapped Files • Monitoring • Network File System (NFS) • PATH • Pipes • Pointers • Relocatable Code • Reset • SETUID • Shell • Sockets • Spooling and Buffering • Streams • Structures • Superuser • System Calls • Unix Signals • User • Using Peripherals